Full Stack Developer Salary in India 2026 – Detailed Guide
Table of Contents
Introduction: Why Full Stack Developers Are Among the Highest Paid in 2026
In 2026, the full stack developer salary in India continues to rank among the highest in the technology sector due to rapid digital transformation across industries. Organizations increasingly seek professionals capable of building complete end-to-end applications—covering frontend interfaces, backend logic, API integrations, databases, cloud deployment, and security. This demand has made full stack developers indispensable to modern product teams.
Companies prefer versatile engineers who can conceptualize, architect, and deliver scalable digital products without heavy dependency on large, specialized teams. This rising demand has also fueled interest in full stack web development in Coimbatore, where learners pursue industry-aligned skills through full stack training Coimbatore programs offered by institutions like VNET Academy.
Today’s digital ecosystem includes mobile platforms, cloud infrastructures, AI-driven systems, and automated CI/CD pipelines. Full stack developers understand how these components work together, enabling faster product delivery, reduced development costs, and higher software quality. As India’s tech ecosystem evolves further in 2026—driven by SaaS growth, global outsourcing, and cloud adoption—the full stack developer salary in India 2026 has witnessed steady growth across experience levels.
Full Stack Developer Salary Overview in India (2026)
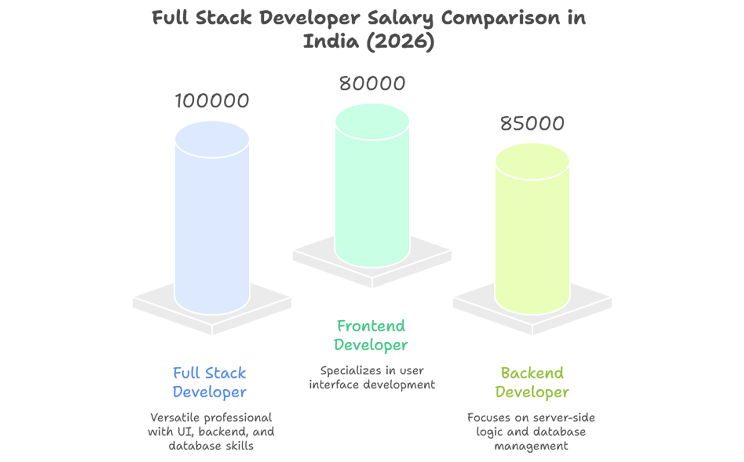
The full stack developer salary in India 2026 has increased significantly due to high demand and a shortage of multi-skilled professionals. While salaries vary based on company type, industry, location, and technology stack, full stack developers consistently earn more than single-skill frontend or backend developers.
Organizations value their ability to handle UI development, backend services, databases, Git workflows, security standards, and cloud deployments. This versatility results in faster development cycles, streamlined maintenance, and reduced communication overhead—factors that directly contribute to higher compensation.According to salary insights published by Glassdoor, the full stack developer salary in India 2026 continues to grow across major tech cities.
Full Stack Developer Salary in India 2026 – Breakdown by Experience
Entry-Level (0–2 Years)
Freshers entering the market in 2026 often receive higher starting packages compared to traditional roles. Skills in React, Angular, Node.js, Express, SQL/NoSQL databases, Git, and deployment tools significantly improve employability. Candidates with strong portfolios and real-time project exposure command better salaries.
Mid-Level (3–6 Years)
Mid-level professionals earn strong salaries due to experience with scalable architectures, microservices, DevOps pipelines, and project ownership. Their ability to solve complex problems and mentor junior developers adds to their market value.
Senior-Level (7+ Years)
Senior developers design and optimize large-scale systems, ensuring performance, security, and scalability. Expertise across multiple frameworks, backend technologies, and cloud platforms places them in premium salary brackets, often with bonuses and equity.Data from AmbitionBox shows that experienced full stack developers earn higher packages in product-based and SaaS companies.
Architect & Lead Roles
Technical leads and solution architects manage system design, cloud infrastructure, DevOps workflows, and strategic engineering decisions. Their leadership responsibilities make them some of the highest-paid professionals in the industry.
Full Stack Developer Salary in India 2026 by Location
Bangalore – India’s Silicon Valley
Home to unicorn startups and global R&D centers, Bangalore offers the highest salaries for full stack developers.
Hyderabad – The Emerging Tech Capital
With rapid expansion of multinational companies and startups, Hyderabad provides lucrative opportunities.
Pune & Mumbai – Product and FinTech Hubs
Pune’s product ecosystem and Mumbai’s fintech dominance drive demand for secure, high-performance applications.
Chennai & Delhi NCR – Enterprise and Startup Mix
These cities offer balanced opportunities across enterprise IT and fast-growing startups with competitive pay.

Salary Based on Technology Stack Expertise (2026)
- MERN Stack Developers – Highly preferred by startups for rapid development
- MEAN Stack Developers – In demand in Angular-based enterprise projects
- Java Full Stack Developers – Strong demand in banking and telecom sectors
- Python & Django Developers – High demand in AI and data-driven platforms
- Cloud-Ready Developers (AWS, Azure, GCP) – Top-tier salaries due to specialization
Salary by Industry & Company Type
- Product-based companies (SaaS, AI startups) offer higher packages and ESOPs
- Service-based companies provide stability and global exposure
- FinTech, HealthTech, EdTech & eCommerce reward domain expertise
- Startups vs MNCs – Startups offer rapid growth; MNCs provide structured careers
Skills That Increase Full Stack Developer Salary in India 2026
Key skills include modern frontend frameworks, backend technologies, cloud platforms, Docker, Kubernetes, CI/CD pipelines, and application security. Strong communication and problem-solving skills further improve career growth. A solid portfolio with real-world projects significantly boosts salary negotiations.
Certifications That Boost Full Stack Developer Salary
Certifications from Google, AWS, Meta, IBM, and Kubernetes validate job-ready skills. Cloud, DevOps, microservices, and cybersecurity credentials help developers stand out in competitive hiring markets.
Freelance Full Stack Developer Earnings in India (2026)
Freelancers with expertise in React, Node.js, and cloud technologies earn premium global rates. Platforms like Upwork, Toptal, Fiverr Pro, and LinkedIn provide international exposure, especially for niche skills such as API security and cloud architecture.
Full Stack Developer Salary Growth Path
Continuous learning enables developers to grow into senior engineers, tech leads, architects, and engineering managers. Those combining AI-assisted workflows with full stack expertise remain highly future-proof.
How Freshers Can Increase Their Full Stack Developer Salary in 2026
Freshers should focus on strong portfolios, internships, open-source contributions, and hackathons. Thorough interview preparation—DSA, system design basics, and project explanations—leads to better salary offers.
Conclusion: Future of Full Stack Developer Salary in India 2026
The full stack developer salary in India 2026 reflects the growing importance of versatile, cloud-ready engineers. With increasing digital adoption across industries, salaries are expected to rise steadily. Developers committed to continuous upskilling and hands-on experience will unlock exceptional earning potential. Training programs like those offered by VNET Academy, providing comprehensive full stack training in Coimbatore, play a key role in building industry-ready professionals.